VPP INTELLIGENCE Hub
If you have news updates to share please contact us.
What is a virtual power plant?
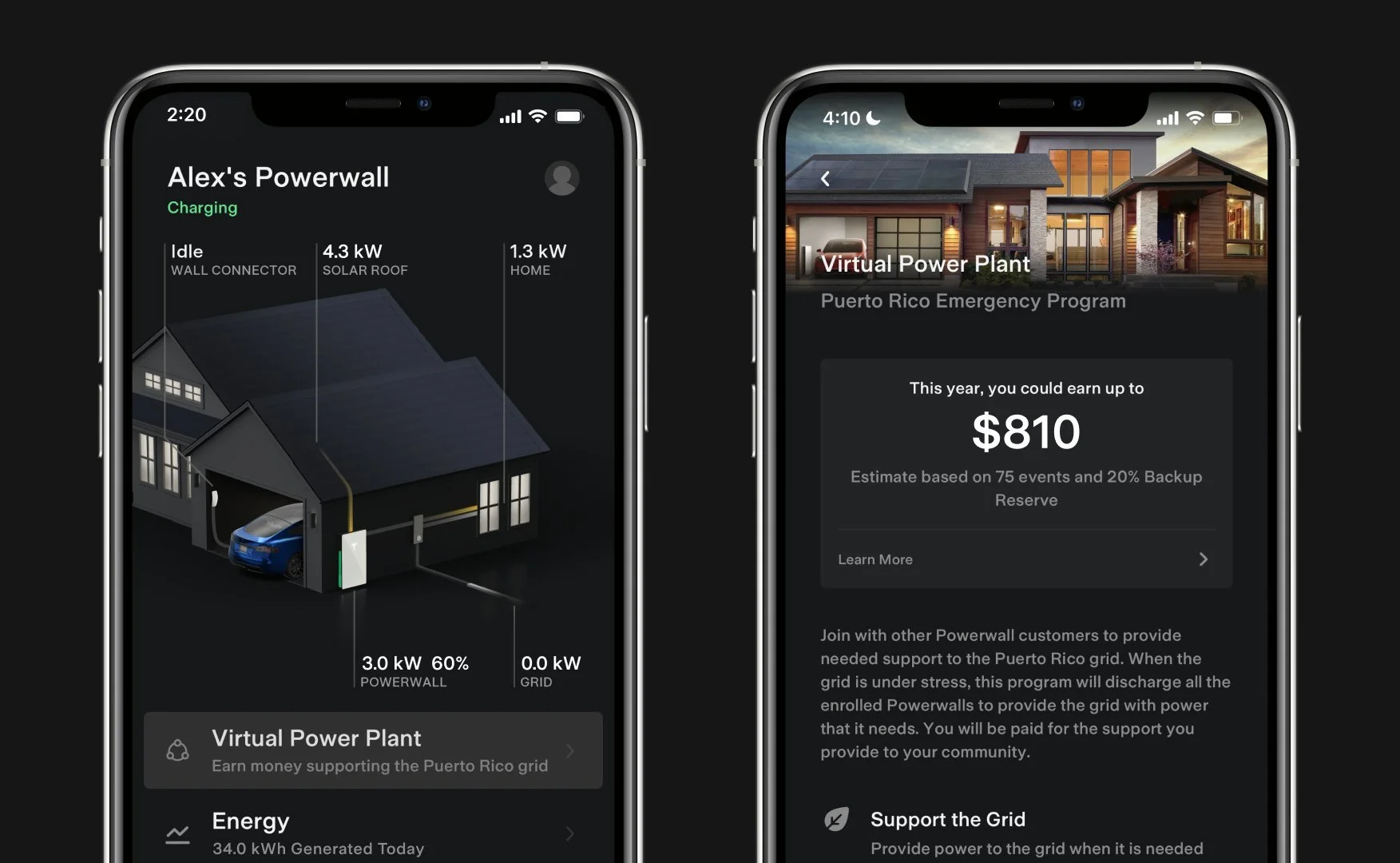
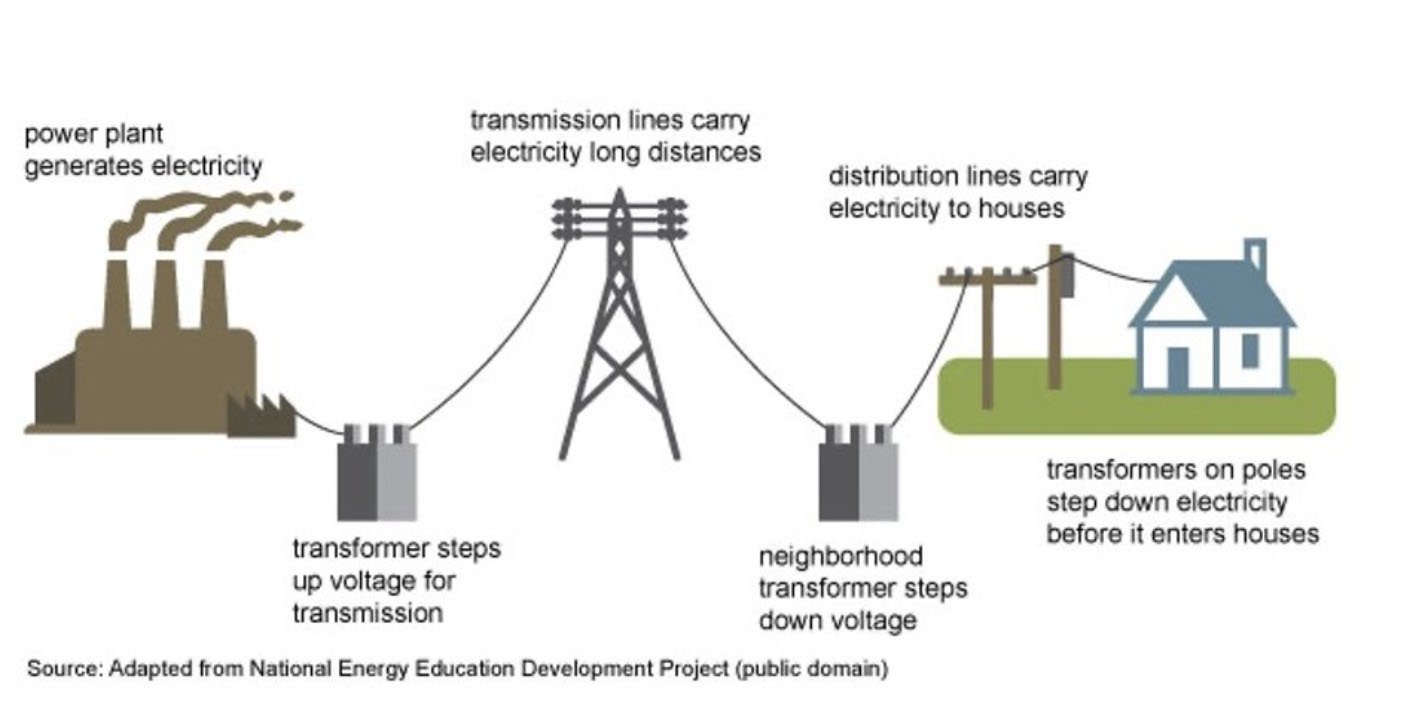
A virtual power plant is a network of energy devices, like rooftop solar, batteries and EVs, that are pooled together to serve the grid. With participants approval the devices can be called on by system operators to share, reduce and store electricity. VPPs are capital and cost-efficient choice for utilities, creating new revenue streams that also benefit consumers, while reducing the overall cost of the electricity system.
Latest news
Latest Research
recent Explainers
library
Tags
- Africa
- Asia
- Australia
- Battery Storage
- COP
- Canada
- China
- Commercial & Industrial
- Costa Rica
- DSR
- Demand-side
- Domestic
- E-mobility
- EV
- Energy
- Europe
- Global
- Hawaii
- Honduras
- International
- Ireland
- Japan
- Latin America
- Middle East
- New Zealand
- Nigeria
- North America
- Renewable Energy
- Residential
- South America
- Taiwan
- Transport
- Turkey
- UAE
- USA
- United Kingdom
- Utilities
- VPPs
- Vietnam
- Zimbabwe
- ancillary services
- data
- energy management
- energy storage
- flexibility
- microgrid
- rooftop solar
- software
- solar pv
Categories
Virtual Power Plants video: ERI@NTU
This video explainer was uploaded by the Energy Research Institute at NTU on 21st October 2020.
Powering a real city with a virtual power plant
Residential solar panels and battery backups are becoming more and more popular as efficiency rises and costs sink. This explosion in distributed solar makes a new idea possible: virtual power plants, or a smart network of individual solar panels that can act like a big power plant when electricity is needed most. And as extreme weather threatens many communities, this idea is arriving in the nick of time.
EV-Based Virtual Power Plants Shift Peak Load and Save Money
A recent study found that electric vehicle (EV) batteries used as a utility virtual power plant (VPP) could shift the entire residential peak load to nighttime hours with only 10% EV market saturation.
Virtual Power Plants Go Global
As distributed energy resources (DER) continue to proliferate, so do the reliability challenges associated with smaller, diverse, and dispersed assets now populating the world’s aging grid infrastructure.
Comprehensive review on structure and operation of virtual power plant in electrical system
Constrained by low capacity and volatility, the rapid growth of distributed energy resources are obviously slowdown resulting in consumption difficulty and investment obstacle. As an effective integration and management technology, virtual power plant (VPP) becomes a suitable cornerstone of renewable energy future development. Based on current scientific research, this study intends to provide a detailed review of VPP from an internal perspective (e.g. energy resources’ integration and operation) to the external aspect including participation in electricity market.
In-depth: How a smart flexible grid could save the UK £40bn
A smart, flexible electricity grid could help the UK cut carbon more cheaply, saving up to £40bn between now and 2050.